Recently, the Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Immunity and Metabolism of our university has published an online research article titled "Hepatitis E Virus ORF1 Polyprotein Harbors a Pocket-like Cavity That Is Vital for Virus Replication and Represents a Novel Antiviral Target" in Advanced Science—a top-tier journal in CAS Category 1 with an Impact Factor (IF) of 14.1. Xuzhou Medical University is the first affiliated unit of the article. Ding Xiaohui, a teacher from the School of Basic Medical Sciences, is the first author, and Professors Wenshi Wang and Hongbo Guo are the corresponding authors. This research work was supported by funds including the National Natural Science Foundation of China and projects from the Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission.
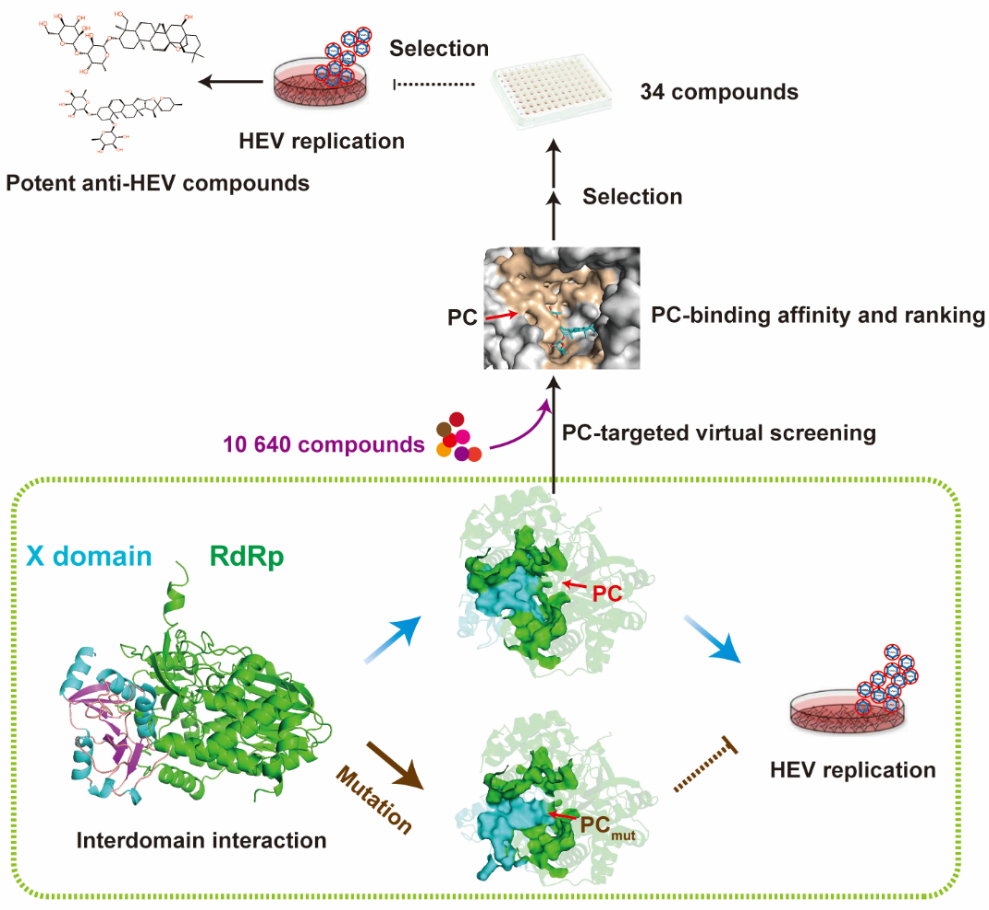
This study reveals, for the first time, a novel structure within the ORF1 polyprotein of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)—a "pocket-like cavity" formed between the X domain and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Functional experiments confirm that this "pocket" is indispensable for viral replication. Based on this discovery, a high-throughput in silico screening platform targeting this "pocket" was further established, verifying that "targeting the cavity at the viral protein interface" can serve as an efficient new antiviral strategy.
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) is the most common cause of acute viral hepatitis worldwide, leading to approximately 20 million infections and 60,000 deaths each year. Currently, there are no FDA-approved specific anti-HEV drugs globally, resulting in limited clinical treatment options. The nonstructural ORF1 polyprotein of the virus is the core engine for its replication; however, its specific mechanism of action has long been a research challenge in the field. This work not only deepens the understanding of the HEV replication mechanism but also lays a theoretical foundation for the development of the first class of specific anti-HEV drugs.
In recent years, guided by major national and local needs, the Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Immunity and Metabolism has focused on research on pathogenic infection and host immunometabolism from an interdisciplinary perspective. Its research findings have been successively published in academic journals such as PNAS, Hepatology, Journal of Clinical Investigation, Microbiome, Cancer Research, Cell Reports Medicine, Theranostics, Gut Microbes, JHEP Reports, Advanced Science, and Nature Communications, and it has been granted more than ten national invention patents.
Original Link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41038801/
First review: Li Li. Second review: Wang Wenshi. Third review: Han Hongliu.