Recently, the Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Immunity and Metabolism of our university has published an online research paper titled “The microbial metabolite desaminotyrosine is a potent antiobesity agent with potential effects on white adipose tissue remodeling in mice” in Gut Microbes (CAS Category 1 Top Journal, IF=11.0). Xuzhou Medical University is listed as the first affiliated institution of the paper. Graduate students Haohan Huang and Longxiang Liao, together with Huimin Bu, a faculty member from the School of Basic Medical Sciences, are identified as the co-first authors. Professors Wei Yanxia and Wang Yugang serve as the corresponding authors. This research was supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation, and the "Jie Bang Gua Shuai" program of Xuzhou Medical University.
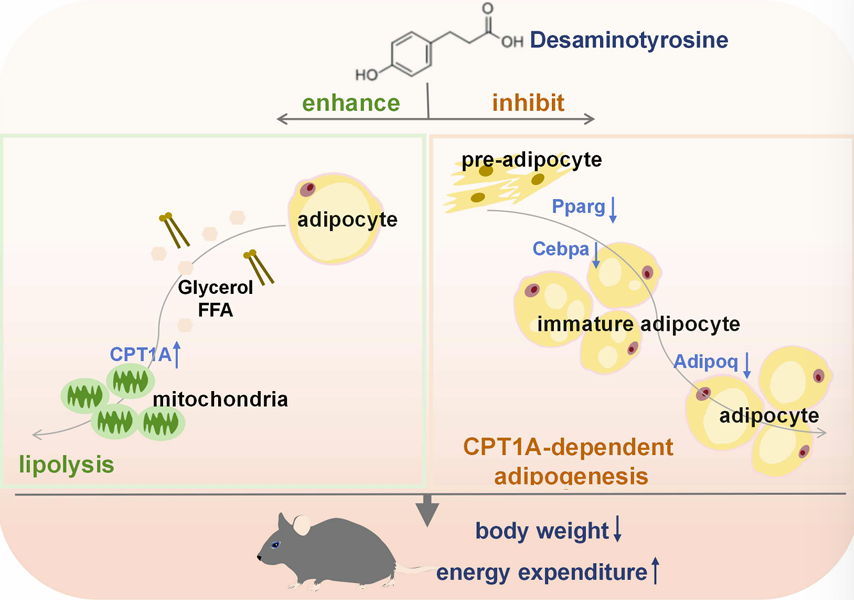
White adipose tissue plays a crucial role in maintaining lipid homeostasis in the body; its dysfunction disrupts lipid balance and induces obesity. Our study revealed that an unhealthy diet, particularly a high-fat diet, leads to intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and impaired tyrosine metabolism, resulting in reduced production of desaminotyrosine (DAT), a microbial metabolite. DAT was found to inhibit weight gain induced by a high-fat diet in mice, which is closely associated with its dual role in regulating white adipose tissue remodeling. On one hand, DAT enhances the autonomous lipid metabolism capacity of mature white adipocytes through sustained lipolysis and upregulation of the expression of CPT1A, a member of the carnitine palmitoyltransferase I family. This effect is particularly pronounced under lipolysis-inducing conditions. On the other hand, DAT blocks the differentiation process of white adipocytes by enhancing the fatty acid oxidation (FAO)-dependent pathway. This work provides new insights for developing pharmacological strategies targeting white adipocyte plasticity to treat metabolic diseases.
In recent years, guided by the major national and local demands, the Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Immunity and Metabolism has conducted a series of basic and applied research on major diseases, based on interdisciplinary approaches and focusing on the interactions between immunity and metabolism, as well as gut microecology and the host. The research findings have been successively published in prestigious academic journals including PNAS, Hepatology, Journal of Clinical Investigation, Microbiome, Cancer Research, Cell Reports Medicine, Theranostics, Gut Microbes, JHEP Reports, Advanced Science and Nature Communications. Additionally, the laboratory has been granted more than ten national invention patents.
Original Link:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41340566/
(First review: Wang Wenshi, Second review: Tang Renxian, Third review: Han Hongliu)